#software deployment model
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Choosing the right cloud deployment model is essential for successfully launching an application. It involves balancing cost and control to optimize the return on investment (ROI) from cloud resources.
Explore the key factors that influence software deployment models to uncover the benefits best suited to your needs.
0 notes
Text
Guidewire Partners With Swiss Re To Reduce Operational Friction Across Insurance Parties

Swiss Re Reinsurance Solutions and Guidewire (NYSE: GWRE) have forged a strategic alliance to use technology to improve connections within the insurance sector. The partnership, which has its roots in a common dedication to insurance innovation and quality, seeks to lessen operational friction for all parties involved in the insurance value chain—risks, insureds, insurers, reinsurers, and intermediaries.
A range of analytics solutions, connectors, and data transmission methods are provided as part of the relationship. The introduction of Swiss Re Reinsurance Solutions' own data models and risk insights into the Guidewire cloud platform marks the beginning of this endeavor. Guidewire's Analytics Manager will make the integration easier and enable the incorporation of pertinent findings into essential insurance activities.
In the face of a dynamic environment and growing complexity in risk assessment, insurers are quickly incorporating advanced analytics into their claims and underwriting processes. This tendency is anticipated to pick even more speed as generative AI becomes more widely used. To share information, gain insights, and ease risk transfer, primary carriers and reinsurers must be able to communicate with one other seamlessly. The goal of Guidewire and Swiss Re's partnership is to reduce friction in insurance procedures by optimizing data availability and predictive model deployment.
Swiss Re Reinsurance Solutions' Chief Executive Officer, Russell Higginbotham, expressed enthusiasm about the collaboration and emphasized Guidewire's worldwide experience in developing technology and analytics for the property and casualty (P&C) insurance industry. The partnership intends to improve the insurance sector's capacity to effectively transfer risks and provide superior customer service.
Read More - https://bit.ly/46dcDNl
#Guidewire Software#Swiss Re#Predictive Model Deployment#Swiss Re Reinsurance Solutions#Guidewire Cloud Platform
0 notes
Text
Elon Musk’s so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) operates on a core underlying assumption: The United States should be run like a startup. So far, that has mostly meant chaotic firings and an eagerness to steamroll regulations. But no pitch deck in 2025 is complete without an overdose of artificial intelligence, and DOGE is no different.
AI itself doesn’t reflexively deserve pitchforks. It has genuine uses and can create genuine efficiencies. It is not inherently untoward to introduce AI into a workflow, especially if you’re aware of and able to manage around its limitations. It’s not clear, though, that DOGE has embraced any of that nuance. If you have a hammer, everything looks like a nail; if you have the most access to the most sensitive data in the country, everything looks like an input.
Wherever DOGE has gone, AI has been in tow. Given the opacity of the organization, a lot remains unknown about how exactly it’s being used and where. But two revelations this week show just how extensive—and potentially misguided—DOGE’s AI aspirations are.
At the Department of Housing and Urban Development, a college undergrad has been tasked with using AI to find where HUD regulations may go beyond the strictest interpretation of underlying laws. (Agencies have traditionally had broad interpretive authority when legislation is vague, although the Supreme Court recently shifted that power to the judicial branch.) This is a task that actually makes some sense for AI, which can synthesize information from large documents far faster than a human could. There’s some risk of hallucination—more specifically, of the model spitting out citations that do not in fact exist—but a human needs to approve these recommendations regardless. This is, on one level, what generative AI is actually pretty good at right now: doing tedious work in a systematic way.
There’s something pernicious, though, in asking an AI model to help dismantle the administrative state. (Beyond the fact of it; your mileage will vary there depending on whether you think low-income housing is a societal good or you’re more of a Not in Any Backyard type.) AI doesn’t actually “know” anything about regulations or whether or not they comport with the strictest possible reading of statutes, something that even highly experienced lawyers will disagree on. It needs to be fed a prompt detailing what to look for, which means you can not only work the refs but write the rulebook for them. It is also exceptionally eager to please, to the point that it will confidently make stuff up rather than decline to respond.
If nothing else, it’s the shortest path to a maximalist gutting of a major agency’s authority, with the chance of scattered bullshit thrown in for good measure.
At least it’s an understandable use case. The same can’t be said for another AI effort associated with DOGE. As WIRED reported Friday, an early DOGE recruiter is once again looking for engineers, this time to “design benchmarks and deploy AI agents across live workflows in federal agencies.” His aim is to eliminate tens of thousands of government positions, replacing them with agentic AI and “freeing up” workers for ostensibly “higher impact” duties.
Here the issue is more clear-cut, even if you think the government should by and large be operated by robots. AI agents are still in the early stages; they’re not nearly cut out for this. They may not ever be. It’s like asking a toddler to operate heavy machinery.
DOGE didn’t introduce AI to the US government. In some cases, it has accelerated or revived AI programs that predate it. The General Services Administration had already been working on an internal chatbot for months; DOGE just put the deployment timeline on ludicrous speed. The Defense Department designed software to help automate reductions-in-force decades ago; DOGE engineers have updated AutoRIF for their own ends. (The Social Security Administration has recently introduced a pre-DOGE chatbot as well, which is worth a mention here if only to refer you to the regrettable training video.)
Even those preexisting projects, though, speak to the concerns around DOGE’s use of AI. The problem isn’t artificial intelligence in and of itself. It’s the full-throttle deployment in contexts where mistakes can have devastating consequences. It’s the lack of clarity around what data is being fed where and with what safeguards.
AI is neither a bogeyman nor a panacea. It’s good at some things and bad at others. But DOGE is using it as an imperfect means to destructive ends. It’s prompting its way toward a hollowed-out US government, essential functions of which will almost inevitably have to be assumed by—surprise!—connected Silicon Valley contractors.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The MS-07B Gouf
In preparation for the invasion of Earth, Zeon forces modified a number of MS-06 Zaku-II F-types for use under the effects of the planet's gravity. The new "J-type" Zaku-IIs featured a number of internal hardware and software changes to enhance their viability on the ground.
The Zaku-II J-Type would be used as a testbed for new developments with the goal of creating a new mass-production mobile suit for use on the ground. And where the Zaku was intended for anti-ship and anti-aerospace combat, this new platform would be built to fight other mobile suits.
Zimmad and Zeonic would both begin working on this new project, directly competing with one another, but eventually coming up with very similar designs. Zeonic moved forward with the YMS-07A Prototype Gouf, and Zimmad presented the YMS-08A High Mobility Test Type.


While Zimmad's design failed to show a significant increase in performance from the Zaku-II J-Type, Zeonic's "Gouf" showed immense promise. The prototype would be picked up and would see a limited production run as the MS-07A Gouf.

The MS-07A was a pre-production model intended for data gathering. The final mass-production model would feature several additional weapon systems, such as an in-built 75mm machine gun in the left manipulator, and a retractable "Heat Rod" on the left forearm.


The Gouf was used to great effect by Zeon captain Ramba Ral, who went toe-to-toe with the Earth Federation's infamous RX-78-2 Gundam.

Among the Ace pilots who used the Gouf as their personal units, Viche Donahue, Silas Locke, and Norris Packard were among the most well-known. All three of these aces would become battlefield legends, with Packard's MS-07B-3 Gouf Custom becoming especially infamous. The machine's equipment proved so effective that it became a common alternate loadout for many Gouf pilots.



The MS-07 would be customized for a variety of roles and theaters, with many of these variants seeing further developments of their own.



Notable among these was the MS-07W Gouf Combined Test Type, which featured a miniaturized Dopp fighter serving as its cockpit. The development of the machine was heavily influenced by data gathered from the Federation's RX-series of mobile suits. Namely, their "Core Block" system.


The Gouf would also see another fork, being developed into the MS-07H Gouf Flight Type. While both prototypes made use of thermonuclear rocket engines, the final version used thermonuclear jet engines, allowing for greater efficiency in atmospheric flight.



The MS-07B saw further refinement into the MS-07C. While not much is known about its specifications, there are at least three known variants. A number of Goufs were acquired by Zimmad and used as testbeds for systems to be incorporated into the MS-09 Dom series of mobile suits. These Goufs were MS-07Cs.



And finally, in UC 120, nearly 50 years from the initial deployment of the original machine, Mars Zeon would develop and deploy the OMS-07RF RF Gouf. While externally resembling the MS-07B, the OMS-07-RF was a completely new machine which could also operate in space, unlike its predecessors.

The MS-07B Gouf was originally designed by Kunio Okawara for the 1979 Anime "Mobile Suit Gundam".
This article was a request! Requests are always welcome!
I am so terribly sorry for the delay in getting this post out! It's been a very hectic few months, but I'm hoping to get back in the flow of things!
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQL Server 2022 Edition and License instructions
SQL Server 2022 Editions:
• Enterprise Edition is ideal for applications requiring mission critical in-memory performance, security, and high availability
• Standard Edition delivers fully featured database capabilities for mid-tier applications and data marts
SQL Server 2022 is also available in free Developer and Express editions. Web Edition is offered in the Services Provider License Agreement (SPLA) program only.
And the Online Store Keyingo Provides the SQL Server 2017/2019/2022 Standard Edition.
SQL Server 2022 licensing models
SQL Server 2022 offers customers a variety of licensing options aligned with how customers typically purchase specific workloads. There are two main licensing models that apply to SQL Server: PER CORE: Gives customers a more precise measure of computing power and a more consistent licensing metric, regardless of whether solutions are deployed on physical servers on-premises, or in virtual or cloud environments.
• Core based licensing is appropriate when customers are unable to count users/devices, have Internet/Extranet workloads or systems that integrate with external facing workloads.
• Under the Per Core model, customers license either by physical server (based on the full physical core count) or by virtual machine (based on virtual cores allocated), as further explained below.
SERVER + CAL: Provides the option to license users and/or devices, with low-cost access to incremental SQL Server deployments.
• Each server running SQL Server software requires a server license.
• Each user and/or device accessing a licensed SQL Server requires a SQL Server CAL that is the same version or newer – for example, to access a SQL Server 2019 Standard Edition server, a user would need a SQL Server 2019 or 2022 CAL.
Each SQL Server CAL allows access to multiple licensed SQL Servers, including Standard Edition and legacy Business Intelligence and Enterprise Edition Servers.SQL Server 2022 Editions availability by licensing model:
Physical core licensing – Enterprise Edition
• Customers can deploy an unlimited number of VMs or containers on the server and utilize the full capacity of the licensed hardware, by fully licensing the server (or server farm) with Enterprise Edition core subscription licenses or licenses with SA coverage based on the total number of physical cores on the servers.
• Subscription licenses or SA provide(s) the option to run an unlimited number of virtual machines or containers to handle dynamic workloads and fully utilize the hardware’s computing power.
Virtual core licensing – Standard/Enterprise Edition
When licensing by virtual core on a virtual OSE with subscription licenses or SA coverage on all virtual cores (including hyperthreaded cores) on the virtual OSE, customers may run any number of containers in that virtual OSE. This benefit applies both to Standard and Enterprise Edition.
Licensing for non-production use
SQL Server 2022 Developer Edition provides a fully featured version of SQL Server software—including all the features and capabilities of Enterprise Edition—licensed for development, test and demonstration purposes only. Customers may install and run the SQL Server Developer Edition software on any number of devices. This is significant because it allows customers to run the software on multiple devices (for testing purposes, for example) without having to license each non-production server system for SQL Server.
A production environment is defined as an environment that is accessed by end-users of an application (such as an Internet website) and that is used for more than gathering feedback or acceptance testing of that application.
SQL Server 2022 Developer Edition is a free product !
#SQL Server 2022 Editions#SQL Server 2022 Standard license#SQL Server 2019 Standard License#SQL Server 2017 Standard Liense
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The progeny of “move fast and break things” is a digital Frankenstein. This Silicon Valley mantra, once celebrated for its disruptive potential, has proven perilous, especially in the realm of artificial intelligence. The rapid iteration and deployment ethos, while fostering innovation, has inadvertently sown seeds of instability and ethical quandaries in AI systems.
AI systems, akin to complex software architectures, require meticulous design and rigorous testing. The “move fast” approach often bypasses these critical stages, leading to systems that are brittle, opaque, and prone to failure. In software engineering, technical debt accumulates when expedient solutions are favored over robust, sustainable ones. Similarly, in AI, the rush to deploy can lead to algorithmic bias, security vulnerabilities, and unintended consequences, creating an ethical and operational debt that is difficult to repay.
The pitfalls of AI are not merely theoretical. Consider the deployment of facial recognition systems that have been shown to exhibit racial bias due to inadequate training data. These systems, hastily integrated into law enforcement, have led to wrongful identifications and arrests, underscoring the dangers of insufficient vetting. The progeny of “move fast” is not just flawed code but flawed societal outcomes.
To avoid these pitfalls, a paradigm shift is necessary. AI development must embrace a philosophy of “move thoughtfully and build responsibly.” This involves adopting rigorous validation protocols akin to those in safety-critical systems like aviation or healthcare. Techniques such as formal verification, which mathematically proves the correctness of algorithms, should be standard practice. Additionally, AI systems must be transparent, with explainable models that allow stakeholders to understand decision-making processes.
Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial. AI developers must work alongside ethicists, sociologists, and domain experts to anticipate and mitigate potential harms. This collaborative approach ensures that AI systems are not only technically sound but socially responsible.
In conclusion, the progeny of “move fast and break things” in AI is a cautionary tale. The path forward requires a commitment to deliberate, ethical, and transparent AI development. By prioritizing robustness and accountability, we can harness the transformative potential of AI without succumbing to the perils of its progeny.
#progeny#AI#skeptic#skepticism#artificial intelligence#general intelligence#generative artificial intelligence#genai#thinking machines#safe AI#friendly AI#unfriendly AI#superintelligence#singularity#intelligence explosion#bias
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling The Intricacies Of Excavation: Delving Deeper During Construction
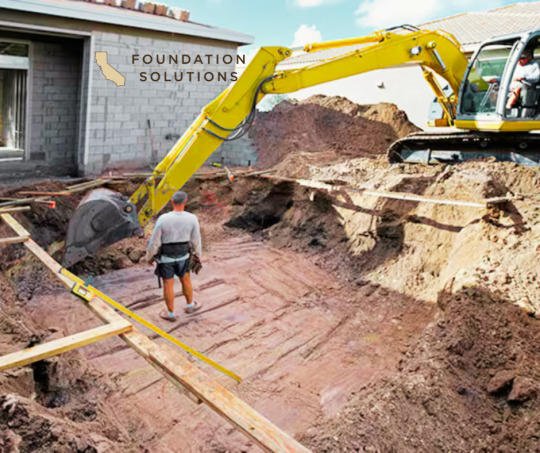

Excavation: the simple term encapsulates a myriad of skills, procedures, and safety measures that contribute significantly to every construction project. Most construction work begins with the careful removal of earth, making a hole or channelling the ground to prepare for the erection of buildings or laying of pipelines. As commonplace as it might seem, excavation is a crucial part of construction that requires extensive planning, expertise and precision.
To begin with, what exactly is excavation? Technically, it’s the process of moving earth, rock or other materials from a site with tools, equipment, or explosives. It includes earthwork, trenching, wall shafts, tunnelling and underground. Yet, in the context of construction, excavation extends beyond mere digging. It modulates the terrain to suit the structural requirement, ensuring the safety and stability of the ensuing structure.
At the heart of every excavation project is the objective to create a stable, safe, and efficient worksite. Basic excavation work typically follows the same series of steps. First, a site assessment is undertaken to determine the composition and stability of the soil, presence of water or rock layers, and any potential hazards. The comprehensive analysis garnered from this assessment then directs the excavation strategy.
Next comes site preparation, which involves clearing the area of any vegetation, debris, or existing structures. This process ensures a clean slate for construction work while minimising the risk of accidents and disturbances during excavation. Benching or sloping techniques could also be implemented on the site to prevent collapse or landslide from happening, thus achieving safety protocol adherence.
The actual excavation work is executed in a carefully measured and precise manner. Whether it’s done manually with shovels and wheelbarrows or mechanically with bulldozers, excavators and backhoes, the work is always carried out meticulously. Technology has indeed become an integral part of excavation, with engineers using software to model excavations prior to deployment, minimising surprises or miscalculations.
Trench excavation is another common practice where a narrow excavation is crafted that is deeper than it is wide. Used mostly for laying pipes, cables and service lines, trench excavation greatly increases the safety of workers by preventing cave-ins and providing easy access to the worksite.
Wet Weather excavation is a challenging scenario frequently encountered on work sites. Here, strategic measures are taken to handle water accumulation. Pumps can be used to remove water, and dewatering methods may be deployed to minimize the water table level.
Post excavation work, structures are erected, pipes are laid, and soil is replaced around the new structure or channel. Again, this is done with extreme care to ensure the stability of the structure and prevent unnecessary exertion of pressure.
In every construction project, the importance of excavation can’t be overstated. It lays the foundation for a safe and successful build. Despite it being a process often overlooked or simplified by laymen, and sometimes perceived as the mundane act of digging, it is, in fact, a scientific procedure replete with precision and tactical stratagems, rivalling the complexity of the structure it prepares ground for.
From the analysis of soil composition to the final touch of replacing the removed dirt, excavation attests to the power of human intervention over nature, moulding the earth to suit the burgeoning demands of urban structures and infrastructures. Understanding its finer details, we may appreciate more deeply the caveats of the construction world and marvel at the impressive structures made possible by these complex and elemental earth movements.
Tagged Construction, Excavation, Foundation Solutions, Intricacies Of Excavation
#Construction#Excavation#Foundation Solutions#Intricacies Of Excavation#foundation repair#foundation contractor#foundation experts#signs of foundation problems#foundation repair near me#foundation services#foundation repair solutions#residential foundation repair services#foundation solution
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Video Agent: The Future of AI-Powered Content Creation

The rise of AI-generated content has transformed how businesses and creators produce videos. Among the most innovative tools is the video agent, an AI-driven solution that automates video creation, editing, and optimization. Whether for marketing, education, or entertainment, video agents are redefining efficiency and creativity in digital media.
In this article, we explore how AI-powered video agents work, their benefits, and their impact on content creation.
What Is a Video Agent?
A video agent is an AI-based system designed to assist in video production. Unlike traditional editing software, it leverages machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to automate tasks such as:
Scriptwriting – Generates engaging scripts based on keywords.
Voiceovers – Converts text to lifelike speech in multiple languages.
Editing – Automatically cuts, transitions, and enhances footage.
Personalization – Tailors videos for different audiences.
These capabilities make video agents indispensable for creators who need high-quality content at scale.
How AI Video Generators Work
The core of a video agent lies in its AI algorithms. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Input & Analysis
Users provide a prompt (e.g., "Create a 1-minute explainer video about AI trends"). The AI video generator analyzes the request and gathers relevant data.
2. Content Generation
Using GPT-based models, the system drafts a script, selects stock footage (or generates synthetic visuals), and adds background music.
3. Editing & Enhancement
The video agent refines the video by:
Adjusting pacing and transitions.
Applying color correction.
Syncing voiceovers with visuals.
4. Output & Optimization
The final video is rendered in various formats, optimized for platforms like YouTube, TikTok, or LinkedIn.
Benefits of Using a Video Agent
Adopting an AI-powered video generator offers several advantages:
1. Time Efficiency
Traditional video production takes hours or days. A video agent reduces this to minutes, allowing rapid content deployment.
2. Cost Savings
Hiring editors, voice actors, and scriptwriters is expensive. AI eliminates these costs while maintaining quality.
3. Scalability
Businesses can generate hundreds of personalized videos for marketing campaigns without extra effort.
4. Consistency
AI ensures brand voice and style remain uniform across all videos.
5. Accessibility
Even non-experts can create professional videos without technical skills.
Top Use Cases for Video Agents
From marketing to education, AI video generators are versatile tools. Key applications include:
1. Marketing & Advertising
Personalized ads – AI tailors videos to user preferences.
Social media content – Quickly generates clips for Instagram, Facebook, etc.
2. E-Learning & Training
Automated tutorials – Simplifies complex topics with visuals.
Corporate training – Creates onboarding videos for employees.
3. News & Journalism
AI-generated news clips – Converts articles into video summaries.
4. Entertainment & Influencers
YouTube automation – Helps creators maintain consistent uploads.
Challenges & Limitations
Despite their advantages, video agents face some hurdles:
1. Lack of Human Touch
AI may struggle with emotional nuance, making some videos feel robotic.
2. Copyright Issues
Using stock footage or AI-generated voices may raise legal concerns.
3. Over-Reliance on Automation
Excessive AI use could reduce creativity in content creation.
The Future of Video Agents
As AI video generation improves, we can expect:
Hyper-realistic avatars – AI-generated presenters indistinguishable from humans.
Real-time video editing – Instant adjustments during live streams.
Advanced personalization – AI predicting viewer preferences before creation.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Wire Harness Production with Automated Crimping Technology

The modern manufacturing landscape increasingly hinges on automation to boost both efficiency and accuracy. A standout innovation driving this transformation is the advent of automatic wire cutting and crimping machines. These sophisticated systems offer a host of compelling advantages, fundamentally reshaping the way wire harnesses are produced.
At the core of these machines' appeal is their ability to combine blazing-fast operation with a remarkably streamlined wire changeover process. Unlike older, more labor-intensive methods, these automated solutions harness cutting-edge Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology. This allows for precise, computer-managed adjustments to both the leading and trailing wire ends, eliminating the need for tedious manual tweaks to cutting and stripping lengths. What's more, the integration of electrically controlled blades drastically simplifies the engineering challenges typically associated with adapting to different wire specifications. This built-in flexibility enables swift transitions between various wire types and dimensions, a critical factor in maximizing production agility and minimizing costly downtime.
Precision and Efficiency Through Digital Control
The operational backbone of automatic wire cutting and crimping machines lies in a fully digital and mathematically driven control system. Every crucial parameter—from cutting and stripping lengths to blade values, semi-stripping settings, and terminal crimping specifications—can be precisely configured via an intuitive interface. This comprehensive digital mastery, particularly the electrically adjustable blades, not only supercharges production efficiency but also positions these machines at the forefront of automation compared to other models. For instance, single-head automatic wire crimping machines are adept at handling multiple tasks: wire cutting, single-end stripping, double-end stripping, and single-end crimping, all executed with remarkable speed, stability, and intelligence. Their touchscreen interface further refines the setup experience, making all adjustments fully digitized and straightforward.
Workforce Optimization and Cost Savings
The advanced automation inherent in these machines empowers manufacturers to optimize their workforce deployment. By taking over repetitive and intricate tasks, these systems free up human capital, allowing employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities. This shift often translates into significant reductions in overall operational costs. Another key benefit is the modular design of these machines. Their reliance on standardized components not only simplifies initial setup but also dramatically cuts down on ongoing maintenance expenses, thanks to readily available and easily replaceable parts. Equipped with cutting-edge electrical controls and proprietary software, these machines boast a highly user-friendly Human-Machine Interface (HMI). This accessibility means that even operators with minimal specialized training can efficiently manage complex wire processing, including wire and terminal changes, effectively "democratizing" the operation of such sophisticated equipment.
Conclusion
In essence, automatic wire cutting and crimping machines represent a monumental leap forward in manufacturing technology. Their synergy of high-speed performance, CNC-driven precision, electrically controlled blades, and intuitive digital interfaces offers compelling advantages over traditional approaches. These machines stand out across various categories of terminal equipment and have secured widespread adoption in today's market, garnering widespread acclaim from users for their innovative design and robust performance.
For in-depth technical resources on automatic terminal crimping machines, explore our specialized page.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
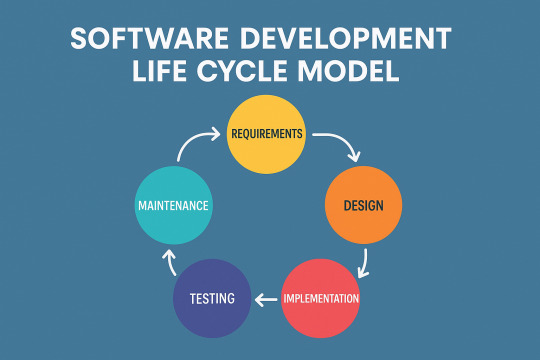
SDLC? Oh, it's the game plan behind every good software.
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle, and it's basically the blueprint developers follow when building software. It breaks the whole thing down into clear steps so nobody’s lost in the sauce.
Here’s the usual flow: 👂 Requirement Gathering – What do users actually want? 🧠 Design – Map out how things should look and work. 💻 Development – Write the code, make the magic happen. 🧪 Testing – Find and squash the bugs. 🚀 Deployment – Send it out into the world. 🛠 Maintenance – Fix issues and keep it fresh.
It’s like building a house, but for software. No one skips to the roof first — you need that foundation.
Different projects might use different SDLC models (like Agile if you like working in sprints, or Waterfall if you’re all about that step-by-step life).
Wanna go deeper? Here’s a great breakdown: 👉 SDLC on PrepInsta
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How does AI contribute to the automation of software testing?
AI-Based Testing Services

In today’s modern rapid growing software development competitive market, ensuring and assuming quality while keeping up with fast release cycles is challenging and a vital part. That’s where AI-Based Testing comes into play and role. Artificial Intelligence - Ai is changing the software testing and checking process by making it a faster, smarter, and more accurate option to go for.
Smart Test Case Generation:
AI can automatically & on its own analyze past test results, user behavior, and application logic to generate relevant test cases with its implementation. This reduces the burden on QA teams, saves time, and assures that the key user and scenarios are always covered—something manual processes might overlook and forget.
Faster Bug Detection and Resolution:
AI-Based Testing leverages the machine learning algorithms to detect the defects more efficiently by identifying the code patterns and anomalies in the code behavior and structure. This proactive approach helps and assists the testers to catch the bugs as early as possible in the development cycle, improving product quality and reducing the cost of fixes.
Improved Test Maintenance:
Even a small or minor UI change can break or last the multiple test scripts in traditional automation with its adaptation. The AI models can adapt to these changes, self-heal broken scripts, and update them automatically. This makes test maintenance less time-consuming and more reliable.
Enhanced Test Coverage:
AI assures that broader test coverage and areas are covered by simulating the realtime-user interactions and analyzing vast present datasets into the scenario. It aids to identify the edge cases and potential issues that might not be obvious to human testers. As a result, AI-based testing significantly reduces the risk of bugs in production.
Predictive Analytics for Risk Management:
AI tools and its features can analyze the historical testing data to predict areas of the application or product crafted that are more likely to fail. This insight helps the teams to prioritize their testing efforts, optimize resources, and make better decisions throughout the development lifecycle.
Seamless Integration with Agile and DevOps:
AI-powered testing tools are built to support continuous testing environments. They integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling faster feedback, quick deployment, and improved collaboration between development and QA teams.
Top technology providers like Suma Soft, IBM, Cyntexa, and Cignex lead the way in AI-Based Testing solutions. They offer and assist with customized services that help the businesses to automate down the Testing process, improve the software quality, and accelerate time to market with advanced AI-driven tools.
#it services#technology#software#saas#saas development company#saas technology#digital transformation#software testing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Software Development Life Cycle
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic process used to build software applications with quality and efficiency. It outlines a series of phases like planning, analysis, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance that guide developers from an idea to a fully functional product. Each SDLC model offers a different approach to managing these phases, based on the project's complexity, goals, and flexibility needs. Understanding the available models helps teams choose the right path for smooth and effective software development.
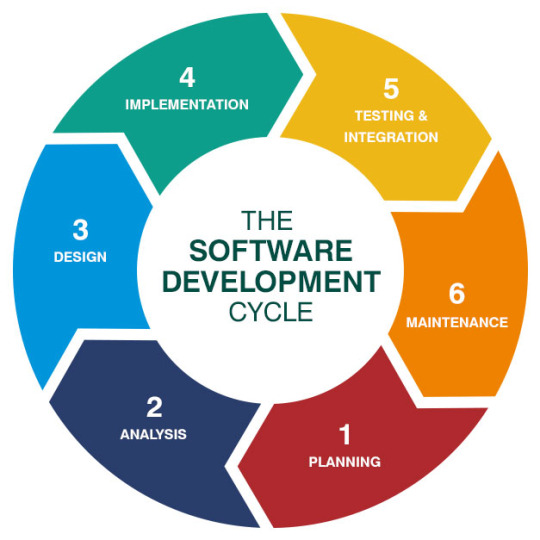
Key SDLC Models:
Waterfall Model: A simple and linear approach where each phase is completed before the next one starts. It works best when requirements are clear and fixed.
Agile Model: Focuses on flexibility and iterative progress. It allows constant feedback and adaptations throughout the development cycle.
Spiral Model: Combines elements of both design and prototyping with a focus on risk analysis. It's ideal for large, high-risk projects.
V-Model: An extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes testing at every stage. Each development phase has a directly associated testing phase.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Effective XMLTV EPG Solutions for VR & CGI Use
Effective XMLTV EPG Guide Solutions and Techniques for VR and CGI Adoption. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, effective xml data epg guide solutions are essential for enhancing user experiences in virtual reality (VR) and computer-generated imagery (CGI).
Understanding how to implement these solutions not only improves content delivery but also boosts viewer engagement.
This post will explore practical techniques and strategies to optimize XMLTV EPG guides, making them more compatible with VR and CGI technologies.
Proven XMLTV EPG Strategies for VR and CGI Success
Several other organizations have successfully integrated VR CGI into their training and operational processes.
For example, Vodafone has recreated their UK Pavilion in VR to enhance employee training on presentation skills, complete with AI-powered feedback and progress tracking.
Similarly, Johnson & Johnson has developed VR simulations for training surgeons on complex medical procedures, significantly improving learning outcomes compared to traditional methods. These instances highlight the scalability and effectiveness of VR CGI in creating detailed, interactive training environments across different industries.
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting VR CGI Technology
Adopting Virtual Reality (VR) and Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) technologies presents a set of unique challenges that can impede their integration into XMLTV technology blogs.
One of the primary barriers is the significant upfront cost associated with 3D content creation. Capturing real-world objects and converting them into detailed 3D models requires substantial investment, which can be prohibitive for many content creators.
Additionally, the complexity of developing VR and AR software involves specialized skills and resources, further escalating the costs and complicating the deployment process.
Hardware Dependencies and User Experience Issues
Most AR/VR experiences hinge heavily on the capabilities of the hardware used. Current devices often have a limited field of view, typically around 90 degrees, which can detract from the immersive experience that is central to VR's appeal.
Moreover, these devices, including the most popular VR headsets, are frequently tethered, restricting user movement and impacting the natural flow of interaction.
Usability issues such as bulky, uncomfortable headsets and the high-power consumption of AR/VR devices add layers of complexity to user adoption.
For many first-time users, the initial experience can be daunting, with motion sickness and headaches being common complaints. These factors collectively pose significant hurdles to the widespread acceptance and enjoyment of VR and AR technologies.

Solutions and Forward-Looking Strategies
Despite these hurdles, there are effective solutions and techniques for overcoming many of the barriers to VR and CGI adoption.
Companies such as VPL Research is one of the first pioneer in the creation of developed and sold virtual reality products.
For example, improving the design and aesthetics of VR technology may boost their attractiveness and comfort, increasing user engagement.
Furthermore, technological developments are likely to cut costs over time, making VR and AR more accessible.
Strategic relationships with tech titans like Apple, Google, Facebook, and Microsoft, which are always inventing in AR, can help to improve xmltv guide epg for iptv blog experiences.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) hold incredible potential for various industries, but many face challenges in adopting these technologies.
Understanding the effective solutions and techniques for overcoming barriers to VR and CGI adoption is crucial for companies looking to innovate.
Practical Tips for Content Creators
To optimize the integration of VR and CGI technologies in xmltv epg blogs, content creators should consider the following practical tips:
Performance Analysis
Profiling Tools: Utilize tools like Unity Editor's Profiler and Oculus' Performance Head Hub Display to monitor VR application performance. These tools help in identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks.
Custom FPS Scripts: Implement custom scripts to track frames per second in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments and optimization.
Optimization Techniques
3D Model Optimization: Reduce the triangle count and use similar materials across models to decrease rendering time.
Lighting and Shadows: Convert real-time lights to baked or mixed and utilize Reflection and Light Probes to enhance visual quality without compromising performance.
Camera Settings: Optimize camera settings by adjusting the far plane distance and enabling features like Frustum and Occlusion Culling.
Building and Testing
Platform-Specific Builds: Ensure that the VR application is built and tested on intended platforms, such as desktop or Android, to guarantee optimal performance across different devices.
Iterative Testing: Regularly test new builds to identify any issues early in the development process, allowing for smoother final deployments.
By adhering to these guidelines, creators can enhance the immersive experience of their XMLTV blogs, making them more engaging and effective in delivering content.
Want to learn more? You can hop over to this website to have a clear insights into how to elevate your multimedia projects and provide seamless access to EPG channels.
youtube
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Continuous Integration: The Backbone of Modern DevOps

Content: Continuous Integration (CI) is more than a buzzword—it’s a discipline that transforms how teams build and deliver software.
In CI, developers frequently merge code changes into a central repository where automated builds and tests are run. This practice catches integration issues early, reduces merge conflicts, and encourages iterative development.
Popular tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, and CircleCI allow developers to automate everything from build processes to security scans. As projects scale, implementing solid CI practices becomes critical for maintaining velocity without sacrificing stability.
Modern service providers often integrate Software Development robust CI pipelines into their project delivery models, ensuring faster, safer deployments for their clients.
By promoting collaboration and early problem detection, continuous integration supports a healthier, more agile development process.
Treat your CI pipeline configuration as code. Version-control it alongside your application code to track changes and maintain consistency across environments.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the realm of artificial intelligence, the devil is in the details. The mantra of “move fast and break things,” once celebrated in the tech industry, is a perilous approach when applied to AI development. This philosophy, born in the era of social media giants, prioritizes rapid iteration over meticulous scrutiny, a dangerous gamble in the high-stakes world of AI.
AI systems, unlike traditional software, are not merely lines of code executing deterministic functions. They are complex, adaptive entities that learn from vast datasets, often exhibiting emergent behaviors that defy simple prediction. The intricacies of neural networks, for instance, involve layers of interconnected nodes, each adjusting weights through backpropagation—a process that, while mathematically elegant, is fraught with potential for unintended consequences.
The pitfalls of a hasty approach in AI are manifold. Consider the issue of bias, a pernicious problem that arises from the minutiae of training data. When datasets are not meticulously curated, AI models can inadvertently perpetuate or even exacerbate societal biases. This is not merely a technical oversight but a profound ethical failure, one that can have real-world repercussions, from discriminatory hiring practices to biased law enforcement tools.
Moreover, the opacity of AI models, particularly deep learning systems, poses a significant challenge. These models operate as black boxes, their decision-making processes inscrutable even to their creators. The lack of transparency is not just a technical hurdle but a barrier to accountability. In critical applications, such as healthcare or autonomous vehicles, the inability to explain an AI’s decision can lead to catastrophic outcomes.
To avoid these pitfalls, a paradigm shift is necessary. The AI community must embrace a culture of “move thoughtfully and fix things.” This involves a rigorous approach to model validation and verification, ensuring that AI systems are robust, fair, and transparent. Techniques such as adversarial testing, where models are exposed to challenging scenarios, can help identify vulnerabilities before deployment.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial. AI developers must work alongside ethicists, domain experts, and policymakers to ensure that AI systems align with societal values and legal frameworks. This collaborative approach can help bridge the gap between technical feasibility and ethical responsibility.
In conclusion, the cavalier ethos of “move fast and break things” is ill-suited to the nuanced and impactful domain of AI. By focusing on the minutiae, adopting rigorous testing methodologies, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we can build AI systems that are not only innovative but also safe, fair, and accountable. The future of AI depends not on speed, but on precision and responsibility.
#minutia#AI#skeptic#skepticism#artificial intelligence#general intelligence#generative artificial intelligence#genai#thinking machines#safe AI#friendly AI#unfriendly AI#superintelligence#singularity#intelligence explosion#bias
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Python Will Thrive: Future Trends and Applications
Python has already made a significant impact in the tech world, and its trajectory for the future is even more promising. From its simplicity and versatility to its widespread use in cutting-edge technologies, Python is expected to continue thriving in the coming years. Considering the kind support of Python Course in Chennai Whatever your level of experience or reason for switching from another programming language, learning Python gets much more fun.

Let's explore why Python will remain at the forefront of software development and what trends and applications will contribute to its ongoing dominance.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Python is already the go-to language for AI and machine learning, and its role in these fields is set to expand further. With powerful libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn, Python simplifies the development of machine learning models and artificial intelligence applications. As more industries integrate AI for automation, personalization, and predictive analytics, Python will remain a core language for developing intelligent systems.
2. Data Science and Big Data
Data science is one of the most significant areas where Python has excelled. Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib make data manipulation and visualization simple and efficient. As companies and organizations continue to generate and analyze vast amounts of data, Python’s ability to process, clean, and visualize big data will only become more critical. Additionally, Python’s compatibility with big data platforms like Hadoop and Apache Spark ensures that it will remain a major player in data-driven decision-making.
3. Web Development
Python’s role in web development is growing thanks to frameworks like Django and Flask, which provide robust, scalable, and secure solutions for building web applications. With the increasing demand for interactive websites and APIs, Python is well-positioned to continue serving as a top language for backend development. Its integration with cloud computing platforms will also fuel its growth in building modern web applications that scale efficiently.
4. Automation and Scripting
Automation is another area where Python excels. Developers use Python to automate tasks ranging from system administration to testing and deployment. With the rise of DevOps practices and the growing demand for workflow automation, Python’s role in streamlining repetitive processes will continue to grow. Businesses across industries will rely on Python to boost productivity, reduce errors, and optimize performance. With the aid of Best Online Training & Placement Programs, which offer comprehensive training and job placement support to anyone looking to develop their talents, it’s easier to learn this tool and advance your career.

5. Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking
With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, cybersecurity is a critical concern for businesses worldwide. Python is widely used for penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and threat detection due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Libraries like Scapy and PyCrypto make Python an excellent choice for ethical hacking and security professionals. As the need for robust cybersecurity measures increases, Python’s role in safeguarding digital assets will continue to thrive.
6. Internet of Things (IoT)
Python’s compatibility with microcontrollers and embedded systems makes it a strong contender in the growing field of IoT. Frameworks like MicroPython and CircuitPython enable developers to build IoT applications efficiently, whether for home automation, smart cities, or industrial systems. As the number of connected devices continues to rise, Python will remain a dominant language for creating scalable and reliable IoT solutions.
7. Cloud Computing and Serverless Architectures
The rise of cloud computing and serverless architectures has created new opportunities for Python. Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure all support Python, allowing developers to build scalable and cost-efficient applications. With its flexibility and integration capabilities, Python is perfectly suited for developing cloud-based applications, serverless functions, and microservices.
8. Gaming and Virtual Reality
Python has long been used in game development, with libraries such as Pygame offering simple tools to create 2D games. However, as gaming and virtual reality (VR) technologies evolve, Python’s role in developing immersive experiences will grow. The language’s ease of use and integration with game engines will make it a popular choice for building gaming platforms, VR applications, and simulations.
9. Expanding Job Market
As Python’s applications continue to grow, so does the demand for Python developers. From startups to tech giants like Google, Facebook, and Amazon, companies across industries are seeking professionals who are proficient in Python. The increasing adoption of Python in various fields, including data science, AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, ensures a thriving job market for Python developers in the future.
10. Constant Evolution and Community Support
Python’s open-source nature means that it’s constantly evolving with new libraries, frameworks, and features. Its vibrant community of developers contributes to its growth and ensures that Python stays relevant to emerging trends and technologies. Whether it’s a new tool for AI or a breakthrough in web development, Python’s community is always working to improve the language and make it more efficient for developers.
Conclusion
Python’s future is bright, with its presence continuing to grow in AI, data science, automation, web development, and beyond. As industries become increasingly data-driven, automated, and connected, Python’s simplicity, versatility, and strong community support make it an ideal choice for developers. Whether you are a beginner looking to start your coding journey or a seasoned professional exploring new career opportunities, learning Python offers long-term benefits in a rapidly evolving tech landscape.
#python course#python training#python#technology#tech#python programming#python online training#python online course#python online classes#python certification
2 notes
·
View notes